18 R Environments
18.1  Environment features
Environment features
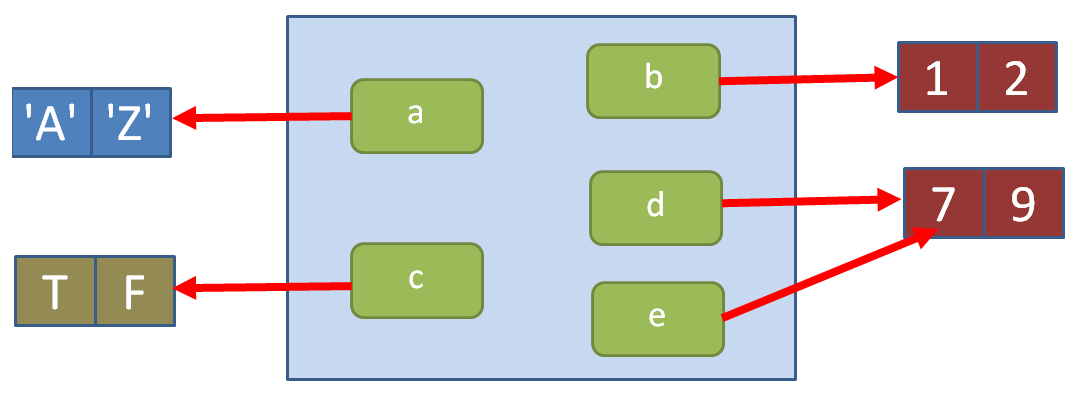
The job of an environment is to associate, or bind, a set of names to a set of values.
An environment may be considered as a bag of names
Each name points to an object stored elsewhere in memory
The objects do not live in the environment; so multiple names can point to the same object. They can also point to different objects that have the same value.
Every name in an environment is unique.
The names in an environment are not ordered.
An environment has a parent.
-
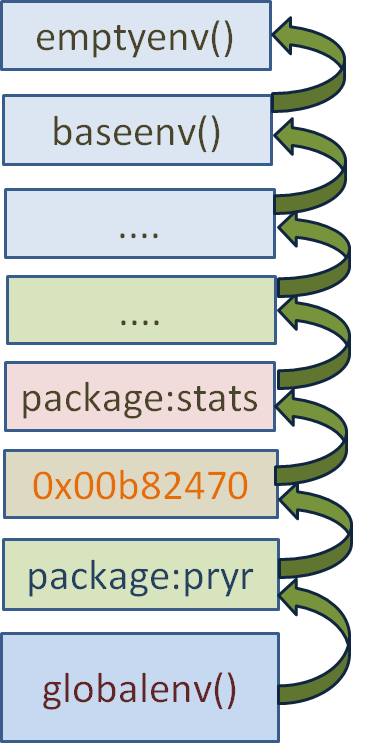
There are four special environments:
The
globalenv(), or global environment, is the interactive workspace. This is the environment in which you normally work. The parent of the global environment is the last package that you attached withlibrary()orrequire().The
baseenv(), or base environment, is the environment of thebasepackage. Its parent is the empty environment.The
emptyenv(), or empty environment, is the ultimate ancestor of all environments, and the only environment without a parent.The
environment()is the current environment.
18.2 All Environments