31 R: browser
31.1  Run in
Run in debug mode
You may wish to jump to a particular location in a function using
browserfunctionThe function interrupts the execution of an expression and allow the inspection of the environment where browser was called from.
You can also run the function optionally with text and condition argument.
Check
?browserfor further details.Once in the browser mode, move around the function as shown below.
Remember to delete the line once you are complete all explorations, otherwise, the script will always jump to debugging mode whne called.
31.2  Debug using
Debug using browser
In the function script, type
browser()in the location of function where you wish to stop for debugging.Source the function and then run the function as shown below.
Once in the browser mode, move around using
n,s,f,c,Qetc.
31.3  Browser window option
Browser window option
In the Debug mode of browser window, you can move around the function using
n,s,f,c,Qetc.If you have a variable names as
n,s,f,c,Q, then useprint(variable_name)You can also use other standard R commands to explore the objects in the function environment.
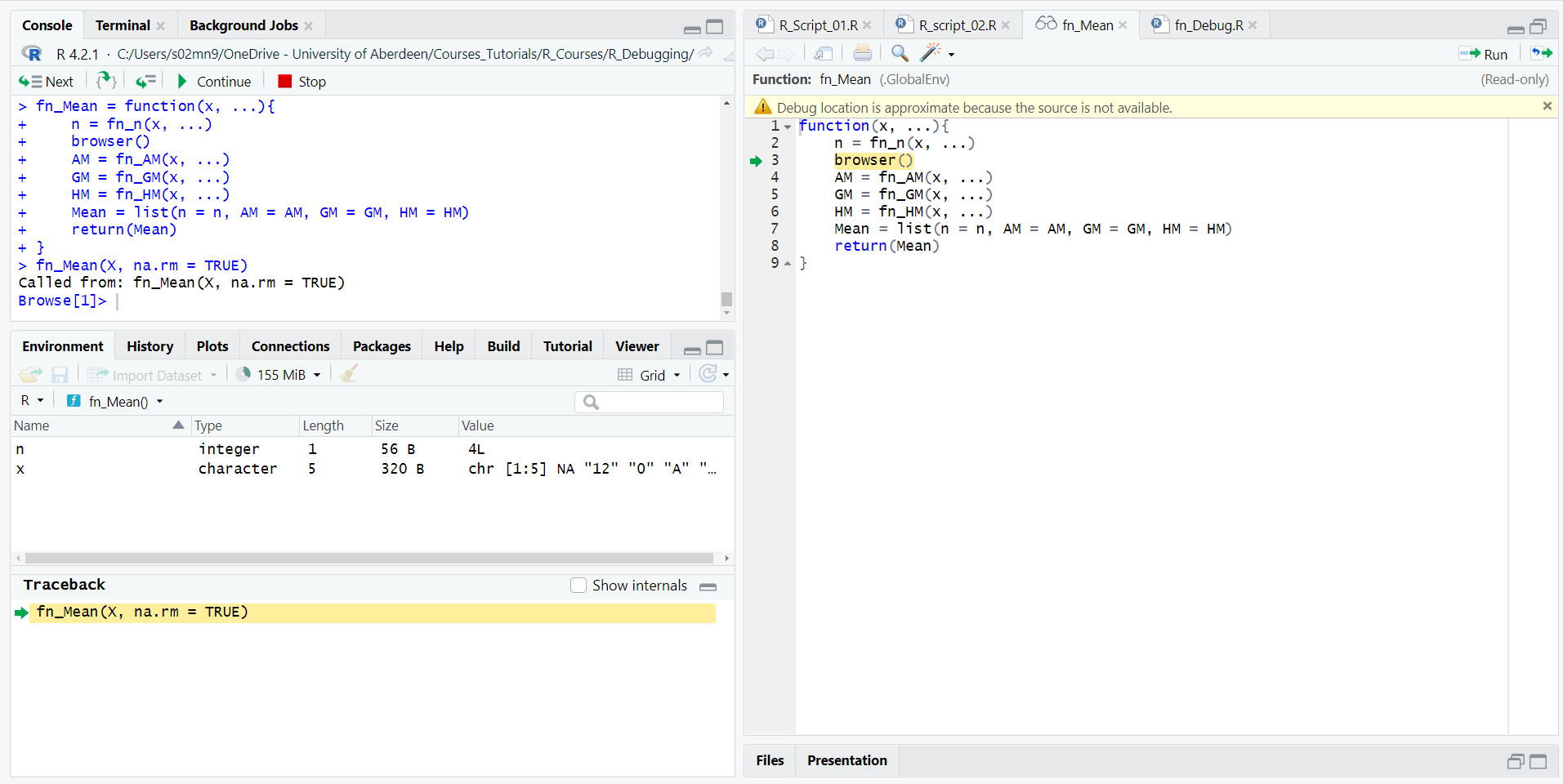
You can also put a browser() within a function and investigate each step of the execution, even if the function does not run into any errors.
Code
X = c(NA, 12, -15, 14, 18)
fn_Mean(X, na.rm = TRUE)