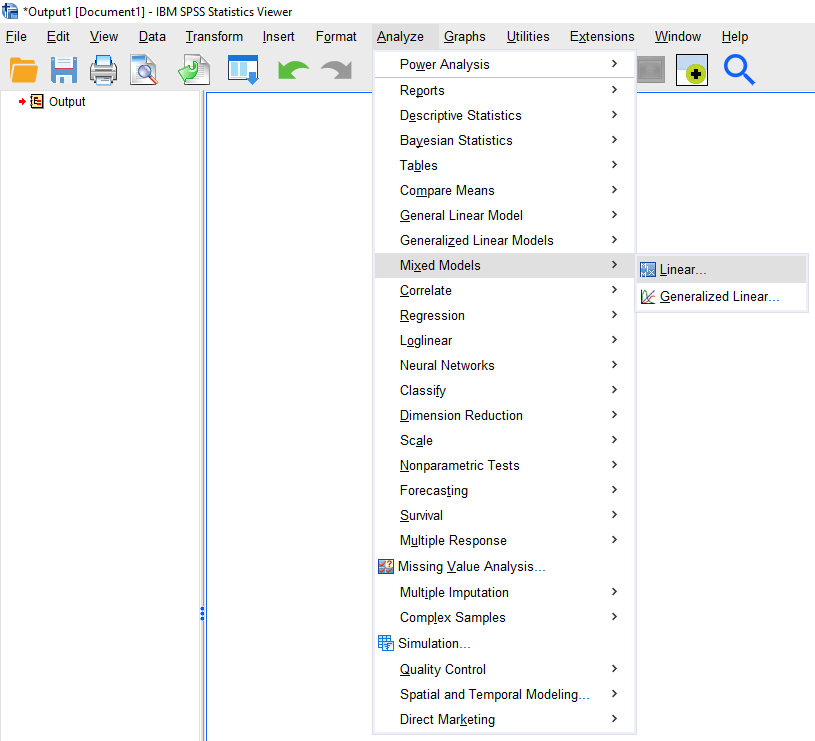
6 LMM: Inputs
6.2 SPSS: Script
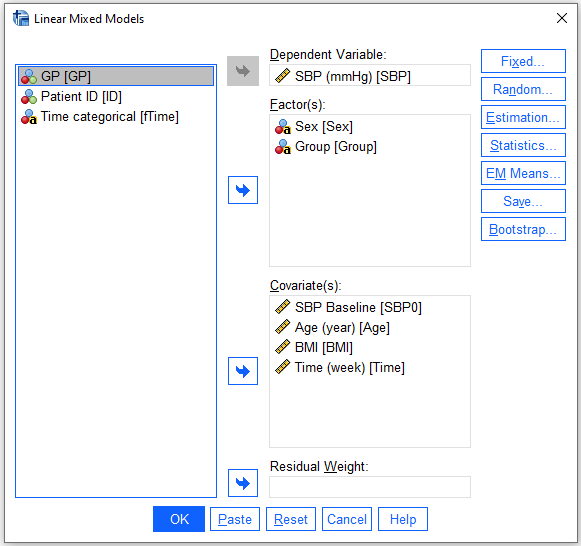
MIXED SBP BY Sex Group WITH SBP0 Age BMI Time
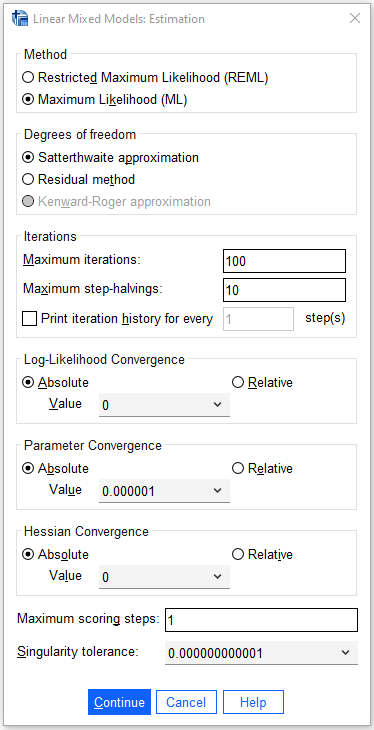
/CRITERIA = DFMETHOD(SATTERTHWAITE) CIN(95) MXITER(100) MXSTEP(10)
SCORING(1) SINGULAR(0.000000000001) HCONVERGE(0, ABSOLUTE)
LCONVERGE(0, ABSOLUTE) PCONVERGE(0.000001, ABSOLUTE)
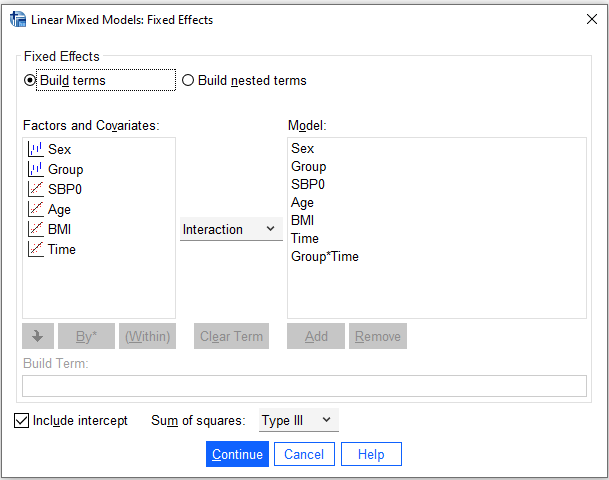
/FIXED = Sex Group SBP0 Age BMI Time Group*Time | SSTYPE(3)
/METHOD = ML
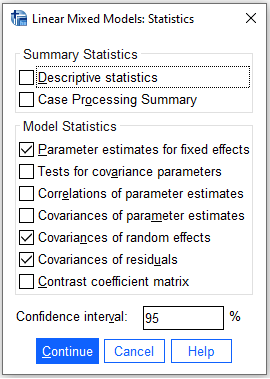
/PRINT = G R SOLUTION
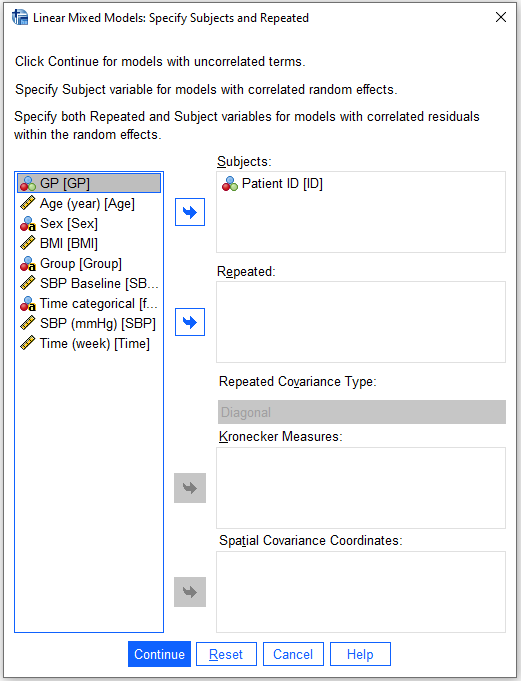
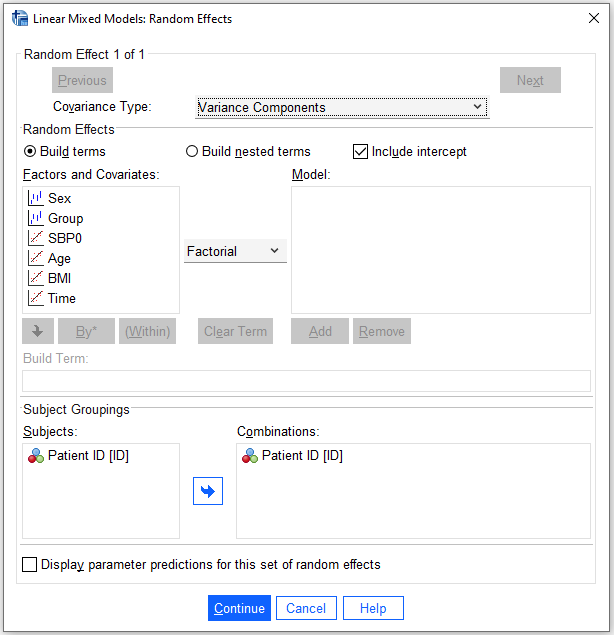
/RANDOM = INTERCEPT | SUBJECT(ID) COVTYPE(VC) 6.3 Summary
The analysis of the data considering the patient as a random effect.